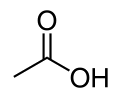
Acetic acid
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Uses
- Generically, as an acid which can be produced fairly easily
- Feedstock for acetic anhydride
- Source acid for all acetate compounds
- Pharm: Ear/nose/throat topical application
Natural occurence
- Main Article: Vinegar
Acetic acid does occur naturally as a secondary metabolite of acetobacter as it consumes ethanol.
- CH3CH2OH + O2{acetobacterCH3COOH + H2OΔH=-490kJ30°C}→
Hazards
- Bronchial & skin irritant
Character
| Temperature (°C) | Mol% water in liquid | Mol% water in vapor |
|---|---|---|
| 100.8 | 0.865 | 0.907 |
| 101.7 | 0.755 | 0.817 |
| 102.4 | 0.675 | 0.770 |
| 103.5 | 0.5725 | 0.678 |
| 104.2 | 0.520 | 0.635 |
| 105.6 | 0440 | 0.556 |
| 107.7 | 0.305 | 0.420 |
- The eutectic point is -27°C / 71.6% (mol/mol) / 88.3% (kg/kg).
Production
Extraction
from vinegar
distillation
- Distill vinegar, preferably at reduced pressure. The water distills over, leaving a proportional increase in concentration. The water bath is important to prevent the possible degradation or oxidation of any acetic acid vapor.
l/l extraction
- Combine vinegar with diethyl ether
- Mix well
- Allow to separate (>90% in the ether layer)
- decant off the hydrocarbon layer
- Distill off the hydrocarbons, leaving acetic acid.
Synthesis
From acetates
via sulfuric acid
- Gather 7 ubm of calcium acetate
- Gather 4 ubm of sulfuric acid
- Combine the acetate and acid, producing a solution of acetic acid and calcium sulfate
- Ca(CH3COO)2 + H2SO4{2 CH3COOH(l) + CaSO4(s)↓otp}→
- Ca(CH3COO)2 + H2SO4
- Distill the solution, precipitating out the calcium sulfate
- CH3COOH(l) + CaSO4(dis){CH3COOH(v) + CaSO4(s)120°C}→
- CH3COOH(l) + CaSO4(dis)
via hydrochloric acid
- As with sulfuric acid, the same reaction can be done with hydrochloric acid producing the more useful calcium chloride as a byproduct.
- Ca(CH3COO)2 + 2 HCl → CaCl2 + 2 CH3COOH
via sodium bisulfate
- Gather equimolar amounts of anhydrous sodium acetate and sodium bisulfate
- Grind and thoroughly mix
- Dry-distill
- NaCH3COO(s) + NaHSO4(s){Na2SO4(s) + CH3COOH(v)heat}→
- NaCH3COO(s) + NaHSO4(s)
- The residue is sodium sulfate
- The distillate is acetic acid
Purification
- Wash with pentane or hexane - immiscible
Testing
(density of solution)-1
========================= 0.049 |
Storage
Disposal
See Also
References
- ↑ SEBASTIANI, E.; LACQUANITI, L. (1967) "Acetic acid-water system thermodynamical correlation of vapor-liquid equilibrium data"
Chemical Engineering Science 22; pp1155-l162. Pergamon Press Ltd.