Penicillin
| |
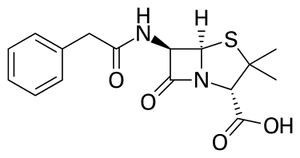
| Chemical formula | {{#Chem:C16H18N2O4S}} |
|---|---|
| Molar Mass(g/mol) | 334.4 |
| NFPA 704 | |
- Penicillin as a class of compounds
Penicillin is a class of medicinal compounds based on a 6-APA framework which contains a beta lactam ring, giving penicillins strong antibiotic activity.
- Penicillin as a specific compound
This page describes the naturally occuring version, penicillin-G, which is a carboxylic acid. It is typically prepared, stored, and administered as a salt with sodium, potassium, or procaine as the cation.
Uses
Primary
- Pharm: The sodium salt and the procaine salt are WHO LEM antibiotics
Natural occurrence
- does occur naturally as a secondary metabolite of penicillium chrysogenum
Hazards
Character
- penicillin G has an oral bioavailability of around 30%, which means that 70% of the dose you take is excreted in urine.
- Amoxicillin oral bioavailability is roughly 95%.
Production
Extraction
- Important
- Scaling
A typical course of Penicillin G for an adult is (125 to 312 milligrams [mg]) every four to six hours for 10 to 14 days, for a total 5g to 25g of penicillin consumed. As far as wild strains go, the Peoria strain from which all modern strains are derived was the best of many wild strains examined. In proper media, it produced 150mg of penicillin per liter of growth media. If we assume assume that "random strains" will yield a tenth of that, or 15mg per liter, they would require more than 1000L (approximately one metric ton) of fermentation broth to be produced and processed for one course of the antibiotic.
- Penicillin Production
- US patent 2399840 "Method for the isolation of penicillin from aqueous solutions"
Link courtesy Google - Make Penicillin at home
courtesy Doom and Bloom. local copy
Synthesis
Although extraction of penicillin G is far more practical, it can be synthesized[1]
Testing
Purification
Storage
Disposal
See Also
References
- ↑ US patent 3047467 "Process for the preparation of penicillins"
Link courtesy Google
